How Overt & Covert Technology Prevents Counterfeiting for Your Business
What happens after the product leaves your purview may be hurting your brand–even though it has absolutely nothing to do with the quality of your wares. Counterfeiting and diversion are very real issues for all industries, with the fallout ranging from loss of brand equity and reputation to physical threats to unwitting consumers.
But how do you get started mitigating this risk? And where do you look to acquire the knowledge you need to best protect your business?
A comprehensive brand protection program needs strong technology
There are a lot of approaches to anti-counterfeiting. In this post, we’ll cover:
- Covert anti-counterfeiting approaches
- Overt anti-counterfeiting approaches
- Pros and cons of each
- Real-world examples
- How to tackle product authenticity to protect your consumers
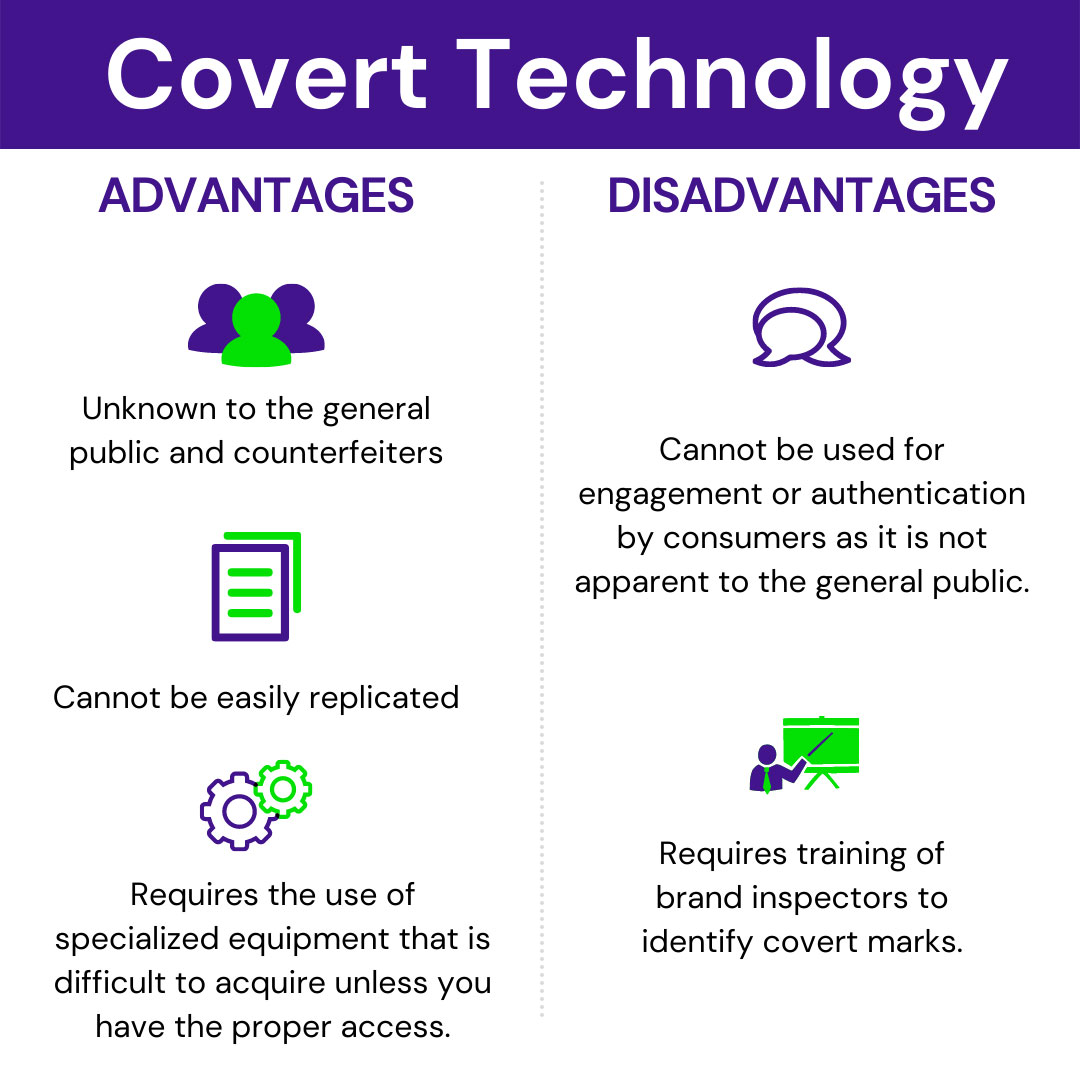
What is Covert Anti-Counterfeiting Technology?
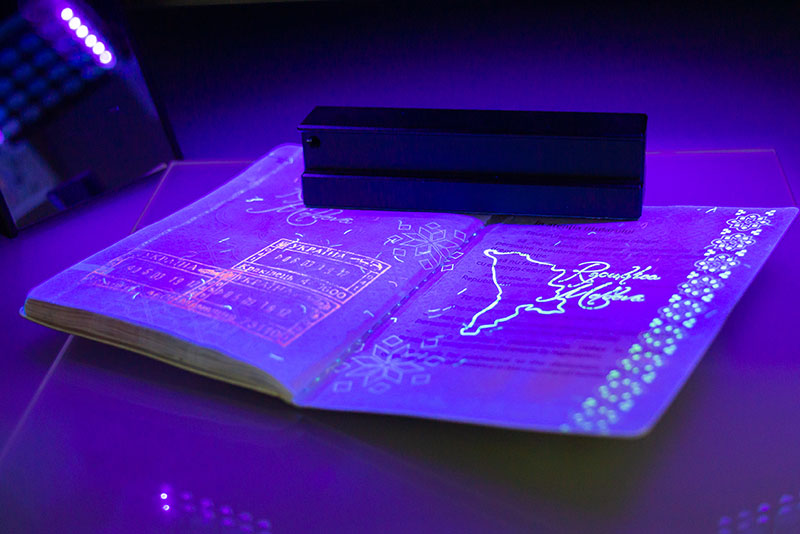

Here are just a few examples of covert brand protection solutions deployed in the field. Note that this technology is intended for off-the-shelf applications, forensic analysis, or purpose-built approaches.
- Microtext – also known as micro printing, is printing characters or symbols at a very small scale, so small that it is unreadable to the human eye. Think of a line of text reduced to the size that it appears like a solid line on the packaging. It is difficult to replicate the characters in digital printing, helping to address counterfeiting issues.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Blacklight Ink – UV Blacklight Ink can not be seen in sun or traditional indoor lighting but when exposed to an ultraviolet lamp one can see a printed image that’s not otherwise visible under normal lighting conditions. UV inks have been used for many decades on security documents and are now commonly found on posters, hand stamps for nightclub entry, toys and games, and even tattoos. Because of UV inks’ long history of use across so many diverse markets and wide availability to purchase, it’s now relatively easy for counterfeiters to detect and replicate, and therefore its value for brand protection and anti-counterfeiting programs has been significantly diminished.
- Taggants – While an actual ink mark may either be visible or invisible to the human eye, a taggant additive is only readable with a special device. Taggants provide an invisible fingerprint on product packaging or the product itself. Printing imbued with a unique taggant is extremely difficult to replicate.
- Intentional defect – This security measure is as its name suggests–an error made on purpose to stump counterfeiters. An example would be an intentional misspelling in micro text or a reoccurring misprint in a sequence of characters. For instance, on a check signature line, the line might actually be microtext but it looks like a line to the human eye. When you magnify the image it may say ‘Global Savings Bank’ over and over. However, one spot in the repeating words might be misspelled by leaving a letter out, adding an extraneous letter, or inverting a letter.
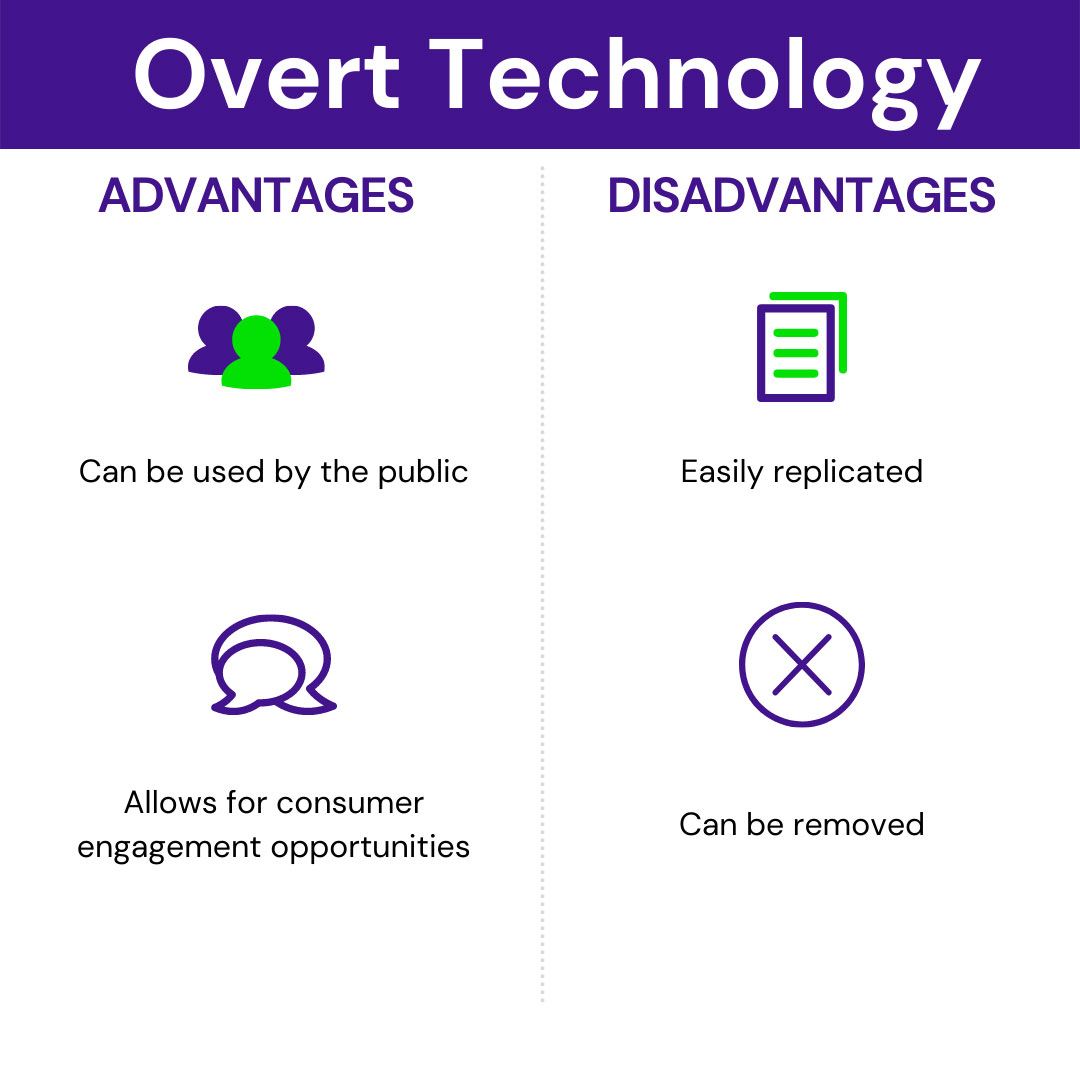
What is Overt Anti-Counterfeiting Technology?

Examples of overt solutions include the below list.
- Holograms are three-dimensional images incorporating some illusion of multidimensional (usually 3D) construction, apparent depth, or spatial separation. Just like UV inks’, holograms have been around for decades. In fact, they have been the de facto overt security feature on credit cards, driver’s licenses, and licensed merchandise for many years. Historically, holograms were extremely difficult to accurately replicate, which made them an excellent overt security feature. However, given the advances in technology, traditional holograms are now being easily counterfeited. In an effort to mitigate this, brand owners and other users of holograms are often combining additional brand protection technologies like unique serialization and covert inks with these images. While this increases the effectiveness of a hologram it also adds cost, which is a consideration as you formulate a brand protection and anti-counterfeiting strategy.
- Guilloché patterns are intricate, interwoven images. Think of complex spirograph patterns. Formed with one of two lines, these repetitive patterns prevent duplication.
- Barcodes are probably one of the most commonly seen overt solutions. These machine-readable codes are in the form of numbers and a pattern of parallel lines of varying widths, printed on and identifying a product.
- QR (quick response) codes are a type of 2D barcode that is used to provide easy access to information through a smartphone. In this process, known as mobile tagging, the smartphone’s owner points the phone at a QR code and opens a barcode reader app that works in conjunction with the phone’s camera.
- NFC (near-field communication) tags use silicon components or integrated circuits (IC) attached to antennas and embedded in labels or other packaging allowing consumers to interact with the product to determine authenticity. NFC tags can be read by newer smartphones and other devices via radio signals when they are held in close proximity to one another. NFC tags do not require a line of sight to read the data encoded on them, which is a benefit over barcodes and QR codes. This benefit should be carefully measured against the significantly increased cost compared to barcodes. Another potential issue is the risk that the chip connected to the antenna breaks, which would render the NFC tag unreadable.
Overt vs Covert Technology | Creating Multilayered Solutions with VerifyMe
As you can see, there are significant positives to both brand protection approaches. It makes sense then to advocate for a layered approach that combines covert and overt security measures. By incorporating a blended application of these solutions, you are creating a significant barrier to counterfeiting and product diversion–taking the best steps you are able to to ensure that your company and your brand thrive.
Layered visible and invisible security offers important benefits. Notably, it is even more secure than only utilizing one method. Applying multiple anti-counterfeiting measures also makes it even more difficult to replicate your security methods. Ensuring consumers are receiving real and not suspect products provides value to your company by confirming people are having the expected experience with your product, hopefully resulting in repurchase and possibly even evangelizing its quality.
One tip to keep in mind is to make some of the anti-counterfeiting marks easy to find overt codes. If the entities seeking to do harm to your brand find it simple to locate codes, chances are they will stop there and not seek out the more sophisticated covert security features. Examples of these overt marks include hologram images on passports, driver’s licenses, identification cards, and more.
How VerifyMe can help you fight counterfeits?
As overt & covert specialists, who help with product authentication and customer engagement, VerifyMe is uniquely positioned to understand your challenges and help you identify the approach that makes the most sense for your brand. Our patented and proprietary solutions have been used to help solve counterfeiting and diversion challenges and improve product-level customer engagement across markets and around the world. Some of the markets we serve include:
Regardless of product or industry, with our bespoke solutions put together by experts with decades of experience, we have a way to help you ensure that your consumers are interacting with an authentic brand experience from your company.
Our solutions and solution components include overt and covert technologies. Select what you want to achieve and learn about our offerings.
- Authentication – Get multiple levels of protection, including tamper-resistant labels, QR codes, NFC chips, and ultra-secure invisible inks and pigments. When you combine high security with customer engagement you are able to protect your brand and gather business intelligence. Our invisible pigments are impossible for criminals to detect or remove and can be integrated into packaging or directly on the product.
- Engagement – Meet your customers where they are and connect products and customers instantly with QR codes and NFC chips. By taking the next step and turning consumer authentication into brand building, your company can take advantage of a huge opportunity to build relationships, while also capturing valuable data to confirm supply chain security and discover purchase preferences.
- Track and Trace – Know where your product is as it travels through the supply chain, identify if diversion is occurring, and captivate customers at point of purchase and beyond. By using our proprietary ink; embedded, scannable chips; QR code and tamper-evident labels: and serialization, you can gain the insight you need to stop counterfeiting and improve your brand loyalty.